
Non-ferrous metals, in a narrow sense, are also called non-ferrous metals. They refer to all metals except iron (sometimes except manganese and chromium) and iron-based alloys. They can be divided into heavy metals (such as copper, lead, zinc), light metals (such as aluminum, magnesium), precious metals (such as gold, silver, platinum) and rare metals (such as tungsten, molybdenum, germanium, lithium, lanthanum, uranium).
In a broad sense, non-ferrous metals also include non-ferrous alloys, which is based on a non-ferrous metal (usually greater than 50%) and adding one or more other elements. Non-ferrous metals are the basic materials for the development of the national economy. Most industries such as aviation, aerospace, automobiles, machinery manufacturing, electricity, communications, construction, and home appliances are based on non-ferrous metal materials. With the rapid development of modern industry, agriculture and science and technology, non-ferrous metals are becoming more and more important in human development. They are not only important strategic materials and important production material, but also important materials for consumer goods in human life.
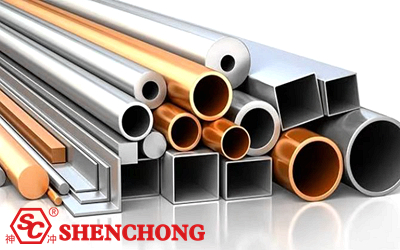
Nonferrous metals refer to all metals and their alloys except iron, chromium and manganese. Compared with ferrous metals (mainly iron and steel), nonferrous metals usually have higher economic value and are widely used in industries such as industry, construction, electronics, aerospace, etc. The following is the classification of nonferrous metals and some common nonferrous metals:
- Light metals: aluminum, magnesium, titanium, lithium, etc. Light metals have low density, good strength and conductivity, and are widely used in aerospace, automobiles, construction and other fields.
- Heavy metals: copper, lead, zinc, nickel, tin, etc. Heavy metals have high density, good mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, and are often used in power, machinery, chemical and other industries.
- Precious metals: gold, silver, platinum, etc. Precious metals have high economic value, good conductivity and corrosion resistance, and are widely used in electronics, jewelry, finance and other fields.
- Rare metals: tungsten, molybdenum, tantalum, niobium, etc. Rare metals have special physical and chemical properties and are often used in high-tech fields such as electronics, nuclear energy, aerospace, etc.
- Rare earth metals: 17 elements such as lanthanum, cerium, neodymium, and samarium. Rare earth metals have unique magnetic, optical and catalytic properties and are widely used in electronics, environmental protection, new energy and other fields.
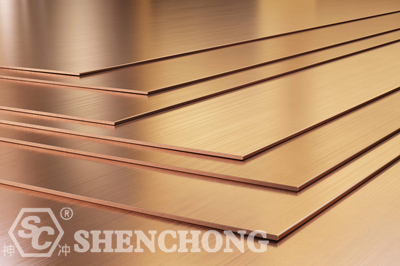
Properties: good electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Applications: wires and cables, motors, electronic components, pipes and heat exchangers, etc.
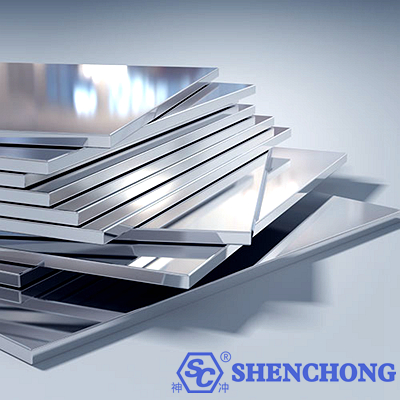
Properties: light weight, good electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance.
Applications: aerospace, construction, transportation, power and electronic products, etc.

Properties: low density and high specific strength.
Applications: aerospace, automobile manufacturing, electronic products and alloy materials, etc.
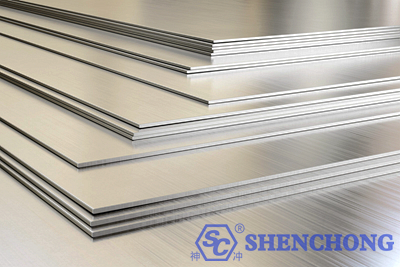
Properties: high strength, light weight, corrosion resistance and high temperature resistance.
Applications: aerospace, medical equipment, chemical equipment and sports equipment, etc.
Properties: corrosion resistance and easy processing.
Applications: galvanized anti-rust, alloy materials, batteries and chemical products, etc.
Properties: high density, corrosion resistance and easy processing.
Applications: batteries, radiation protection materials, pipelines and chemical products, etc.
Properties: good electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, strong ductility.
Applications: electronic components, jewelry, financial investment and medical equipment, etc.

Properties: best electrical and thermal conductivity, good antibacterial properties.
Applications: electronic products, jewelry, mirrors, batteries and medical equipment, etc.
Non-ferrous metals occupy an important position in modern industry and technology. With the development of technology, their application scope and importance are also expanding.
Click here to know other metal materials:
Stainless Steel Surface Treatment And Processing Technology
Alloy Steel Classification: Common Types and Characteristics
Common Surface Treatment Processes for Sheet Metal Materials
Heavy non-ferrous metal alloys, light non-ferrous metal alloys, precious metal alloys, rare metal alloys, etc.. According to the use of the alloys, they can be divided into: deformation (alloys for pressure processing), casting alloys, bearing alloys, printing alloys, cemented carbide, solder, master alloys, metal powders, etc.
Copper and copper alloys, aluminum and aluminum alloys, lead and lead alloys, nickel and nickel alloys, titanium and titanium alloys. When classified by shape, they can be divided into: plates, strips, strips, foils, tubes, rods, wires, and types.
- Non-ferrous smelting products: refers to various pure nonferrous metals or alloy products obtained by smelting methods.
- Non-ferrous processed products (or deformed alloys): refers to various nonferrous semi-finished materials such as tubes, cups, wires, molds, plates, foils, strips, and belts produced by mechanical processing methods.
- Cast non-ferrous alloys: refers to mechanical parts of various shapes formed by direct casting of non-ferrous metal materials by casting methods.
- Bearing alloys: refers specifically to non-ferrous metal materials used to make sliding bearing bushes.
- Hard alloy: refers to a hard tool material made of refractory hard metal compounds (such as tungsten carbide and titanium carbide) as the matrix, cobalt, iron or nickel as the binder, and powder metallurgy (also cast). Its characteristics are better red hardness and wear resistance than high-speed tool steel, such as tungsten-cobalt alloy, tungsten-cobalt-thorium alloy and general-purpose hard alloy.
- Solder: Solder refers to the nonferrous alloy used for welding metal parts.
- Metal powder: refers to powdered nonferrous metal materials, such as magnesium powder, aluminum powder, copper powder, etc.
In the biomedical field, non-ferrous metal materials are widely used due to their excellent biocompatibility, mechanical properties, and photo thermal conversion. For interventional consumables, non-ferrous metals such as titanium, magnesium, tantalum, and zinc meet the requirements of bone repair and vascular remodeling, which are widely used in clinical practice. In the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, non-ferrous metal-based nonmaterial have also demonstrated their application value through a large number of in vitro and in vivo experiments. In addition, metal complex drugs and sensor substrate probes are two other major application areas for non-ferrous metals. In particular, the presence of tens of millions of organic ligands makes metal-organic frameworks and metal complexes more worthy of people's expectations.
In power plant equipment, non-ferrous metal materials are widely used. Commonly used are aluminum and aluminum alloys, copper and copper alloys, titanium and titanium alloys, etc. Aluminum alloys are often used to make heat exchangers, pipes, containers, shells and rivets, etc. Copper alloys are more suitable for making some corrosion-resistant parts, such as turbines, bearings, sleeves, etc.; titanium alloys are more suitable for making condenser pipes, long blades of steam turbines, etc. in thermal power plants.
CNC Front Feeding Shearing Machine For Cobalt Or Nickel Plate
In the field of transportation, the most prominent feature of non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium is their low density. They are the best materials for the manufacture of body shells and other parts of new energy vehicles, and can effectively achieve the lightweighting of new energy vehicles. The application of non-ferrous metals such as aluminum and titanium plays a very important role in the aerospace field. Lightweight materials are the key to reducing the weight of aerospace vehicles such as aircraft, rockets, and satellites, and also provide important support for the safety and energy conservation of aircraft. Nickel, copper, and lead are all non-ferrous metals with high density and good electrical conductivity, so they are mainly used in vehicle power batteries and charging piles. For example, nickel and lead metals can be used to manufacture nickel-hydrogen batteries, lead-acid batteries, and ternary lithium batteries, the latter of which is the mainstream battery type in new energy vehicles.
In the field of construction, non-ferrous metals are widely used in the construction field, such as copper products, aluminum alloy doors and windows, copper wall panels and metal roofs, etc. The use of non-ferrous metals makes buildings more beautiful, safe, durable and energy-saving.
In the field of electronics, non-ferrous metal materials play an important role in the evolution of chip technology. As the size of advanced processes continues to shrink, precious metals and their alloy materials play a key role in achieving small line widths, low resistivity, and high adhesion. After entering the 21st century, a total of more than 40 elements have been added to chip materials, of which about 90% are precious metals and transition metal materials. Gallium and germanium are widely used in semiconductor materials, new energy and other fields. Among them, gallium is called the "new food of the semiconductor industry" and is widely used in photovoltaic, magnetic materials, medical treatment, chemicals, especially wireless communications, LEDs and other fields.
In recent years, photovoltaic, wind power, new energy vehicles, power and energy storage batteries have become the main areas of growth in non-ferrous metal consumption.
Non-ferrous metals are essential basic materials and important strategic materials for the national economy, people's daily life, national defense industry, and the development of science and technology. Agricultural modernization, industrial modernization, national defense, and scientific and technological modernization are inseparable from nonferrous metals. For example, the components or parts required for cutting-edge weapons such as aircraft, missiles, rockets, satellites, and nuclear submarines, as well as cutting-edge technologies such as atomic energy, television, communications, radar, and electronic computers are mostly made of light metals and rare metals among nonferrous metals; in addition, without nonferrous metals such as nickel, cobalt, tungsten, molybdenum, vanadium, and niobium, there would be no production of alloy steel. The use of nonferrous metals in certain applications (such as the power industry, etc.) is also considerable. Many countries in the world, especially industrially developed countries, are competing to develop nonferrous metal industries and increase strategic reserves of nonferrous metals.
Today, non-ferrous metals have become an important material basis for the development of a country's economy, science and technology, and national defense, and are key strategic resources for enhancing a country's comprehensive strength and ensuring national security. As the largest producer of non-ferrous metals, we have made great progress in the field of non-ferrous metal research, especially in the development and utilization of complex low-grade nonferrous metal resources.
For cutting non-ferrous metals in high-efficiency and high-quality, such as cobalt plates and nickel plates, it is not common that the low shearing efficiency to affect the production capacity. Wuxi Shenchong specially made shearing machine can effectively improve the shearing efficiency, ensure the shearing quality, and meet customer shearing requirement. With the continuous advancement of science and the continuous development of industry, Wuxi shenchong CNC high-precision shearing machines are becoming more and more popular.