
Sheet metal structure is the processing and production of thin metal plates.
Thin plate refers to a steel plate whose thickness is much smaller than its length and width. Its transverse bending resistance is poor, and it is not suitable for occasions subjected to transverse bending loads.
Sheet metal is metal in terms of its material, but because of its special geometric shape, the thickness is very small. So the processing technology of sheet metal structural parts has its particularity.
There are three types of processing techniques related to sheet metal structural parts:
(1) Blanking: plate shearing and punching.
(2) Forming: sheet metal bending, folding, hemming and deep drawing.
(3) Connection: welding, bonding, etc.
The structural design of thin plate members should mainly consider the requirements and characteristics of the processing technology. Also, pay attention to the batch size of the artifacts.
The reason why sheet metal structure parts are widely used is that sheet metal has the following advantages:
(1) Easy to deform: In this way, various forms of components can be manufactured with simple processing technology.
(2) The sheet metal components are light in weight.
(3) Small processing volume: due to the high surface quality of the sheet metal and the small dimensional tolerance in the thickness direction, the plate surface does not need to be processed.
(4) It is easy to cut and weld, and can manufacture large and complex components.
(5) The shape is standardized, which is convenient for automatic processing.
Sheet metal refers to the sheet metal whose thickness is much smaller than its length. Because of its special geometric structure and small thickness, small volume, light weight and easy cutting, it can be used to manufacture large and complex parts with high production efficiency and low production cost, and is widely used in various fields.
The processing of sheet metal parts can meet the needs of various mechanical manufacturing in terms of performance and structure, so as to process the final product.
In the 21st century, with the continuous improvement of manufacturing process requirements, in order to continuously optimize sheet metal parts, we must focus on solving the optimization design problem and implement it in the structural design of sheet metal parts.
Sheet metal usually refers to punching a thin metal sheet by hand or through a die, so that it undergoes irreversible plastic deformation to obtain the shape and size required by people. After that, more complex parts can be further formed by welding or machining.
On the premise of satisfying the function of the product, the designed structure should meet some basic requirements, such as easy processing, beautiful appearance, low cost, and so on.
Taking the electrical cabinet door as an example:
The structure of sheet metal parts required by different installation methods is different. The built-in door sheet metal is thinner than the out-mounted door.
All in all, there is no specific sheet metal structure, only sheet metal parts designed according to requirements. This is not only the characteristic of sheet metal parts, but also its design difficulty.
When designing product parts, the problem of easy manufacture must be considered. Try to think of some methods, which can not only make processing easy, but also save materials, increase strength and reduce waste products.
Therefore, designers should pay attention to the following manufacturing matters:
The manufacturability of sheet metal parts refers to the difficulty of parts in punching, bending and stretching. Good technology should ensure less material consumption, less number of processes, simple die structure, high service life and stable product quality.
In general, the biggest impact on the manufacturability of sheet metal parts is the performance of materials, the geometry, size and accuracy requirements of parts.
How to fully consider the requirements and characteristics of processing technology in the structural design of sheet metal components? Here are some design guidelines.
The simpler the geometry of the cutting surface, the more convenient and simple the cutting and blanking. The shorter the cutting path, the smaller the cutting amount.
For example:
A straight line is simpler than a curve.
A circle is simpler than an ellipse and other higher-order curves.
A regular figure is simpler than an irregular figure......
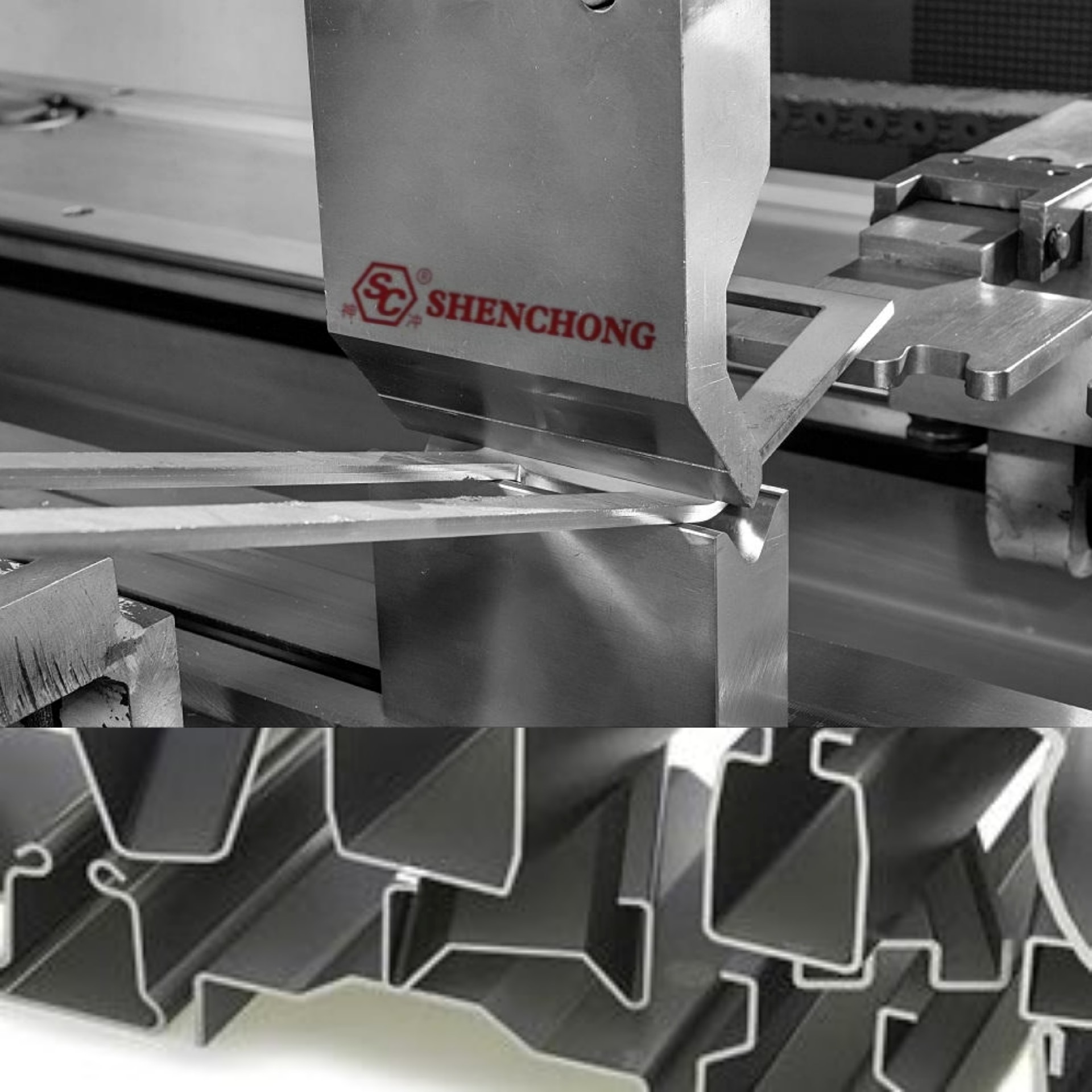

Saving raw material means reducing manufacturing costs. Fragmented scraps are often treated as waste, so in the design of sheet metal components, we should try to reduce scraps as much as possible. Die cutting waste is minimized to reduce material waste. Especially in the blanking of large quantities of components, the effect is remarkable.
The ways to reduce scraps are:
(1) Reduce the distance between two adjacent components.
(2) Arrange cleverly.
(3) Take out the material at the large plane for smaller components.
The bending edge with beveled edge shall avoid the deformation area.
In the design of punching holes on parts, appropriate hole margins and hole spacing should be considered to avoid punching. The minimum distance between the punched edge of the part and the shape is limited depending on the shape of the part and the hole.
When the edge of the punching hole is not parallel to the edge of the part shape, the minimum distance should not be less than the material thickness t. When it is parallel, it should not be less than 1.5t.
The depth and width of the protruding or concave part of the blanking part should generally not be less than 1.5t (t is the thickness of the material). At the same time, narrow and long cuts and too narrow grooves should be avoided in order to increase the edge strength of the corresponding parts of the mold.
When blanking and cutting in the middle of components, there will be the problem of bonding and tightening between tools and components.
Solution:
(1) Leave a certain slope
(2) Cut surface connectivity
When the lap joint is made into a 90° flange by punching in one process, the material selection should be careful not to be too hard. Otherwise, it is easy to break at right-angle bends. The process incision should be designed at the position of the bent edge to prevent cracking at the corner.
With the continuous development of sheet metal industry, today's metal processing technology is diverse. Sheet metal structural part design is a widely used and practical part in processing technology. We need to have a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of this process in order to make better use of it in the future.