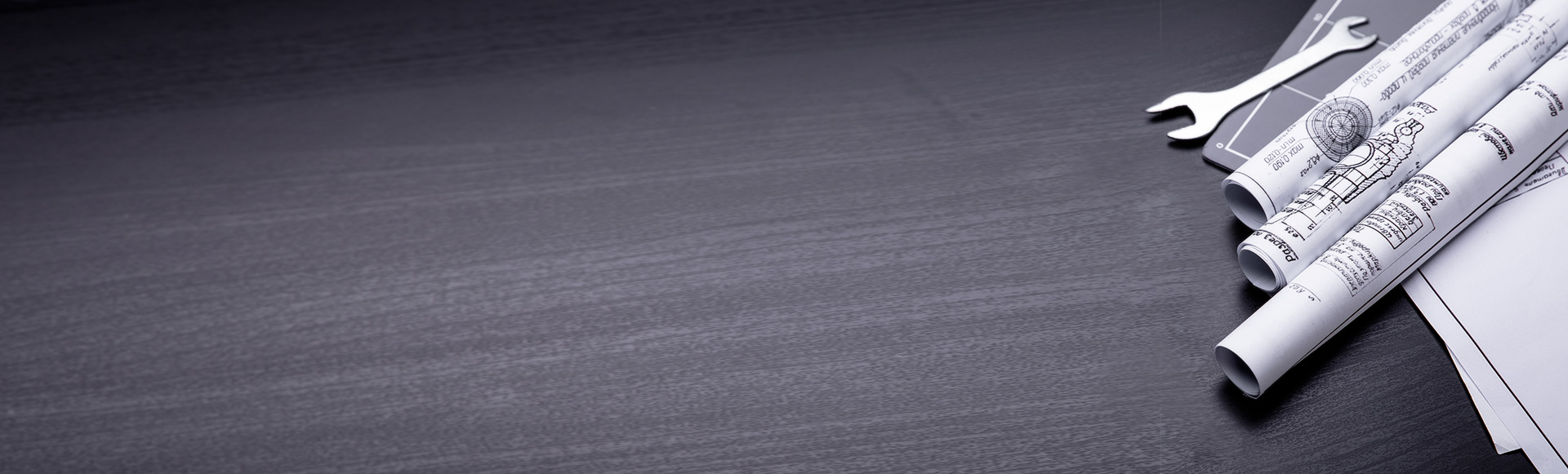

The intelligent welding production line is a modern production system that combines automation technology, robotics, artificial intelligence and industrial Internet of Things (IoT) to improve welding quality, production efficiency and flexibility. It is widely used in automobile manufacturing, shipbuilding industry, engineering machinery, aerospace and other fields.
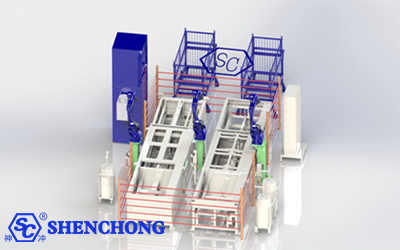
The technological innovation of intelligent welding robots has introduced a comprehensive intelligent production system, covering intelligent sheet metal storage systems, robot automatic loading and unloading systems, intelligent sorting technology, and high-precision press rake bending machines and stamping equipment.
By integrating advanced management and control software, the system can intelligently analyze design drawings, automatically match production needs, and intelligently issue orders to each operation unit, significantly reducing manual intervention and achieving efficient operation of the production line. This process ensures that the products produced meet high standards, high precision and high reliability, while significantly shortening the delivery cycle.
Feature description:
Use welding robots, automatic loading and unloading systems and intelligent transmission equipment to perform tasks such as welding, assembly and handling.
Automatically complete welding path planning, workpiece identification and process adjustment to reduce manual intervention.
Advantages:
Improve production efficiency, reduce labor costs and human errors.
Support 24-hour continuous production to ensure stable production rhythm.
Feature description:
Use visual recognition, laser tracking, sensor monitoring and other technologies to ensure the accuracy of welding position, angle and penetration depth.
Welding parameters (such as current, voltage, speed, etc.) are adjusted in real time to maintain consistent weld quality.
Advantages:
Good weld consistency, reducing welding defects and rework.
Meet high-demand precision welding needs, such as automotive manufacturing and aerospace.
Feature description:
Data analysis, quality prediction and parameter optimization of the welding process based on artificial intelligence algorithms.
Use self-learning and adaptive control technology to automatically adjust the welding process for different working conditions.
Equipment interconnection and remote monitoring are achieved through the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) to support predictive maintenance.
Advantages:
Improve production flexibility and quality control capabilities.
Discover and solve problems in time and reduce downtime.
Feature description:
Use sensors and edge computing devices to collect data such as temperature, current, and molten pool morphology during welding.
Perform big data analysis based on the cloud platform to optimize welding processes and production processes.
Data can be used for quality traceability and production visualization to support decision optimization.
Advantages:
Improve welding quality and consistency, reduce material loss and production costs.
Achieve transparency and traceability of the entire production process.
Feature description:
Support a variety of welding processes (such as arc welding, laser welding, friction welding, etc.) and workpieces of different materials and thicknesses.
By replacing fixtures and adjusting programs, welding tasks of different products can be quickly switched.
Adopting modular design, it is easy to expand and upgrade.
Advantages:
Adapt to small batch and multi-variety production needs.
Reduce production preparation time and equipment investment costs.
Feature description:
Integrate non-destructive testing technology (such as ultrasonic, X-ray, visual inspection, etc.) to automatically identify weld defects.
Online quality monitoring system collects data in real time, intelligently analyzes and alarms.
Supports closed-loop control and automatically adjusts welding parameters based on test results.
Advantages:
Ensure stable weld quality and reduce scrap rate and rework costs.
Ensure that products meet industry standards and customer requirements.
Feature description:
Adopt high-efficiency power supply and green welding process (such as cold welding, stir friction welding, etc.) to reduce energy consumption and exhaust emissions.
Through intelligent management system, rationally plan energy consumption and resource use.
Advantages:
Reduce production costs and meet green manufacturing requirements.
Improve the environmental friendliness and market competitiveness of enterprises.
Feature description:
Reduce production cycle and standby time through automation and intelligent means.
Data-driven production optimization and predictive maintenance to avoid equipment downtime caused by sudden failure.
Advantages:
Increase production capacity and equipment utilization, and reduce maintenance and operating costs.
Quickly respond to market demand and shorten delivery cycle.
The main features of the intelligent welding production line are automation, intelligence, flexibility and high precision. Through data-driven and AI technology, it not only improves welding quality and efficiency, but also achieves energy conservation, environmental protection and cost control.
The intelligent welding production line combines automation technology, robotics, artificial intelligence and industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), with the core purpose of improving welding quality, production efficiency and flexibility. The following are the main components and functions of the intelligent welding production line:
Core function:
Perform automated tasks such as welding, assembly and handling.
Components:
Industrial robot body: Multi-axis (usually 6 axes or more) robot arm, supporting processes such as spot welding, arc welding, laser welding, etc.
Welding tools and end effectors: including welding guns, fixtures, cutting heads, etc.
Welding power supply and controller: Provide stable welding current and parameter control.
Features:
Programmable, high repeatability, adaptable to complex welding paths.
Core function:
Real-time perception and feedback of the status and data of the welding process.
Components:
Visual sensor: used for weld detection, welding position identification and tracking.
Laser sensor: Detect weld morphology, gap, angle, etc.
Temperature and arc sensor: Monitor welding temperature, penetration and arc stability.
Features:
Automatically adjust welding parameters through real-time analysis of sensor data.
Core function:
Centralized management and intelligent control of production line equipment.
Components:
Programmable logic controller (PLC): Perform basic control tasks such as welding path, speed, time, etc.
Upper computer and SCADA system: Monitor the operation status of the entire production line, data collection and visualization.
AI algorithm and edge computing equipment: Used for data analysis, anomaly detection, and adaptive adjustment.
Features:
Support self-learning and adaptive control to improve welding accuracy and efficiency.
Core function:
Equipment interconnection and data collection, support remote monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Components:
Sensor network and communication protocol: Use 5G, industrial Ethernet, OPC UA and other protocols to achieve high-speed data transmission.
Cloud platform and big data analysis: Store and process welding data, perform trend analysis and predictive maintenance.
MES system (manufacturing execution system): production planning, task scheduling and resource management.
Features:
Data-driven production optimization and intelligent decision-making.
Core function:
Support multiple welding processes, improve process applicability and welding quality.
Components:
Welding process equipment: arc welder, laser welder, friction welder, etc.
Intelligent welding software: used for path planning, parameter setting and optimization.
Jigs and tooling equipment: ensure positioning and stability during welding.
Features:
Adapt to welding requirements of different materials, thicknesses and structures.
Core function:
Support safe collaboration and flexible production between people and machines.
Components:
Collaborative robot (Cobot): equipped with force feedback and safety sensors, suitable for complex welding tasks.
Human-machine interface (HMI): touch screen, voice control and other methods for easy operation and monitoring.
Safety system: grating, emergency stop device, anti-collision, etc. to ensure safe production.
Features:
Improve production flexibility and adapt to small batch and customized production.
Core function:
Automated detection and quality traceability to ensure welding quality.
Components:
Non-destructive testing equipment: ultrasonic, X-ray, infrared detection, etc.
Online quality monitoring system: Real-time detection of weld quality and defects, automatic alarm and repair.
Traceability system: Based on barcode, RFID and other technologies, full-process product traceability.
Features:
Improve yield rate, reduce rework and scrap rate.
Core function:
Responsible for the automatic transmission and circulation of workpieces to ensure production rhythm.
Components:
AGV trolley and conveyor belt: used for the transportation and position calibration of workpieces.
Warehousing and sorting system: Automatic storage and distribution of workpieces to be welded.
Intelligent scheduling system: Optimize material flow path based on production plan and task priority.
Features:
Ensure production continuity and rhythm, and improve logistics efficiency.
The components of the intelligent welding production line include both hardware equipment (such as robots, sensors, welding equipment) and software systems (such as intelligent control, quality management, IIoT platform). They work together to ensure the efficiency and high quality of welding production.
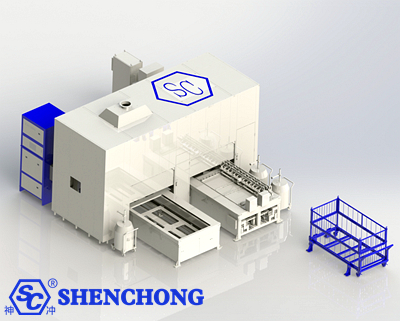
Intelligent welding production lines have been widely used in many industries due to their high efficiency, precision and automation. The following are some typical application scenarios:
Application scenarios: body welding, chassis welding, exhaust system welding, parts assembly
Spot welding robot: used for spot welding of body in white (BIW) to ensure the consistency and strength of welding points.
Arc welding and laser welding: used for high-precision welding of doors, exhaust systems, fuel tanks and other parts.
Intelligent perception system: using visual recognition and laser sensors to ensure accurate weld position and automatically adjust the welding path.
Advantages: improve production efficiency, stable welding quality, and reduce labor costs.
Application scenarios: welding of large structural parts such as excavators, loaders, cranes, etc.
Arc welding robot: used for welding thick plates and large steel structures to ensure strength and precision.
Intelligent control and monitoring: real-time monitoring of temperature and weld quality, and automatic adjustment of welding parameters.
Flexible production unit: adapt to the welding needs of products of different specifications and improve production flexibility.
Advantages: Stable welding quality, improved efficiency, and adaptable to small-batch and multi-variety production.
Application scenarios: welding of carriages, chassis, bogies, and body frames
Laser-arc hybrid welding: suitable for long welds of aluminum alloys, stainless steel and other materials with different thicknesses.
High-precision welding robot: uses trajectory control and sensor systems to ensure uniform welds.
Intelligent detection and repair: uses ultrasonic waves, X-rays and other means to detect weld quality and automatically repair defects.
Advantages: Ensure weld strength and quality to meet the safety and stability requirements of high-speed trains.
Application scenarios: welding of large-area steel structures such as hulls, decks, and bulkheads
Multi-layer and multi-pass welding technology: to meet the strength requirements of thick plate welding, intelligent path planning is used.
Automated welding of long welds: through gantry welding robots, continuous welding of long welds is achieved.
Real-time monitoring and intelligent control: monitor temperature, penetration depth, etc., and automatically adjust current and speed.
Advantages: Greatly reduce welding hours and improve weld quality and efficiency.
Application scenarios: welding of complex structural parts such as wings, fuselages, turbine blades
Electron beam welding and laser welding: suitable for welding of lightweight materials such as titanium alloys and aluminum alloys.
High-precision visual guidance system: ensure welding accuracy of complex curved surfaces and avoid stress concentration.
Data-driven quality control: analyze welding data collected by sensors to predict welding defects.
Advantages: improve welding strength and lightweight level, meet high safety requirements.
Application scenarios: welding of small structural parts such as shells, heat sinks, connectors
Laser welding and micro-arc welding: suitable for precision welding of thin plate materials such as stainless steel and aluminum alloys.
Flexible automated production line: supports rapid switching and production of multiple varieties and small batches.
Intelligent detection and traceability system: quality traceability and detection through QR codes and sensors.
Advantages: high welding accuracy, reduced deformation, and increased production speed.
The intelligent welding production line has achieved a comprehensive improvement in production efficiency, welding quality and cost control through the integration of automation, intelligence and flexibility. It has demonstrated strong competitiveness in industries such as automobiles, construction machinery, and rail transit.