
Nowadays, the application of automation technology in product production is perfect! It has also derived a professional term - automated production line.
Before introducing the design process of automated production line, let's first briefly understand what is automated production line.
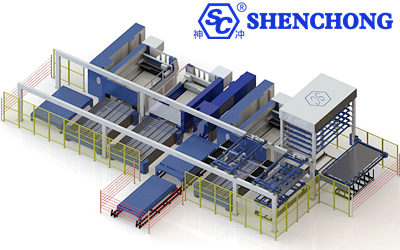
Automated production line is developed on the basis of assembly line. It not only requires various mechanical processing devices on the line to automatically complete the predetermined processes and products of the process, but also requires that the loading and unloading of workpieces, the transportation between processes, the sorting and even the packaging of workpieces can be carried out automatically. Make it work automatically according to the prescribed procedures.
Drive technology, mechanical technology, sensor technology, control technology, human-machine interface technology, network technology
Through some auxiliary devices, various mechanical processing devices are connected in a process sequence, and the hydraulic, pneumatic, and electrical systems are controlled to connect the actions of each part to complete the predetermined production task.
The design and assembly of automated production lines involve highly specialized processes, including demand analysis, system design, component selection, software programming, debugging and testing, and integration of some applications into the entire production system. Among them, system design is a crucial step that ensures the efficient, precise and continuous operation of the production line.
Demand analysis and planning are the first steps in the design of automated production lines. It is necessary to clarify the production process, production efficiency goals, quality control requirements and budget of the product. After that, the overall layout of the production line is planned according to the demand, and the appropriate combination of automated equipment is selected, such as industrial robots, conveyor belts, assembly stations, etc.
Before designing an automated production line, a comprehensive analysis of the production process needs to be conducted. This includes production goals, required output, product specifications, working environment and other requirements. Through communication and research with customers, the design team can fully understand customer needs and convert them into actual technical requirements.
After the demand analysis is completed, the planning team will plan the preliminary design plan for the automated production line based on the information obtained. This plan will cover the overall layout of the production line, including equipment configuration, layout of work sites, material flow, and necessary manual intervention points.
In this stage, the design team will propose some preliminary automated production line design solutions based on the results of the demand analysis. These solutions may include different options such as using different equipment, process flows and layouts. The design team will evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, compare and screen them, and finally determine the most suitable conceptual design solution.
Designers need to determine the key components of the automated production line, such as sensors, control systems, actuators, and mechanical structures. This stage also requires determining the requirements for data collection and monitoring systems to ensure data accuracy and real-time feedback during the production process.
The design team will further refine the conceptual design and convert it into a detailed engineering design. This includes determining the specific specifications of the required equipment, selecting the appropriate control system, determining the layout and process flow of the production line, etc. In addition, detailed calculations and evaluations of the energy consumption and work efficiency of the automated production line are required.
Choosing the right machines, components and parts is very important to ensure the smooth operation of the production line. When choosing, not only performance, efficiency and compatibility should be considered, but also long-term maintainability and cost-effectiveness. The core components of the automated production line usually include robots, PLCs (programmable logic controllers), various sensors, actuators and interactive interfaces.
After the detailed design is completed, the design team will communicate with suppliers and purchase the required equipment and systems. Supply chain management plays a decisive role in this stage. They are also responsible for installing the equipment and ensuring its normal operation. This stage requires close cooperation and coordination to ensure that the equipment is installed and debugged according to the design requirements.
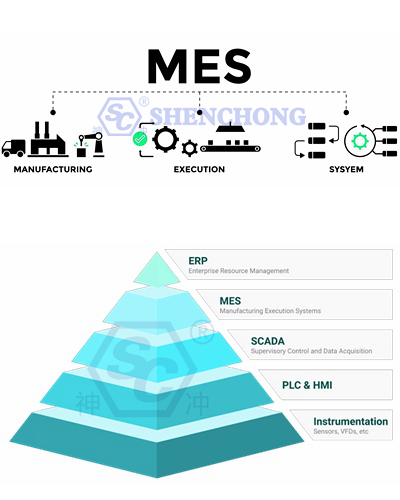
The efficiency and accuracy of automated production lines depend largely on the quality of the software. Control software usually requires programming to coordinate workstations and machine operations. Programming requires not only precise control of all mechanical movements, but also data collection and real-time monitoring.
The software must also be able to integrate with the manufacturing execution system (MES) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, so that the information flow and logistics of the entire enterprise can be synchronized, and the level of intelligent production can be improved.
Sheet Metal Automated Production: IT Infrastructure To Intelligent Manufacturing System
The last step of the entire production line is integration, which combines and integrates all the scattered components and subsystems into a collaborative whole. The integration work includes the integration of mechanical, electrical, and control systems to ensure that they can interoperate and communicate in the entire automation system.
End-user training will also be conducted at this time to ensure that operators understand the working principles and maintenance procedures of the system. Proper use and maintenance are the key to ensuring stable operation and extending the life of the production line.
Once the automated production line is put into use, the design team will be responsible for training operators and providing necessary maintenance and care instructions. They will teach operators how to use the equipment correctly, how to perform routine maintenance, and solve equipment failures and problems. Through training and maintenance, the continuous operation and efficient operation of the automated production line can be guaranteed.
Designing an automated production line requires a series of rigorous design processes. From demand analysis to final training and maintenance, each step is crucial. Only through comprehensive analysis, reasonable design and effective testing can we ensure that the automated production line can achieve the expected results.
The maintenance plan should include daily inspections, preventive maintenance and emergency failure response. At the same time, developing a long-term upgrade roadmap can help companies continuously optimize the performance of the production line and ensure the long-term return on investment.
In summary, the design and assembly of an automated production line is a complex engineering project that requires a high level of planning, design, execution, testing and maintenance. The core focus includes a comprehensive understanding of requirements, precise system design, appropriate component selection, high-quality software programming, careful debugging and testing, and smooth integration and maintenance. Through these steps, an efficient, flexible and sustainable automated production line can be established.
Click here to know more about:
How To Get Automated Production Lines? Enterprise Conditions
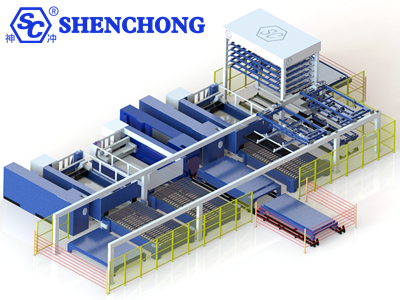
The design principles of automated production lines include process optimization, equipment selection, process improvement, etc. Designers will analyze each link in the production process and optimize the process according to production requirements and goals to ensure the efficient operation of the production line. At the same time, appropriate equipment and technology are selected to ensure the stability and high degree of automation of the production line.
In the assembly of the production line, multiple factors need to be considered. First, it is necessary to clarify the type and specifications of the products to be produced, and ensure that the equipment and processes used for assembly can meet the product quality and requirements.
Secondly, it is necessary to rationally plan the layout of the production line, consider the coordination and parallel operation between processes, so as to improve production efficiency. It is also necessary to consider the training and operating specifications of personnel to ensure the safety of the production line and the production capacity of employees.
There are several key links that require special attention during the assembly process of the automated production line.
The first is the assembly and debugging of the equipment, including the connection and setting of each device to ensure communication and coordination between devices.
The second is the software configuration and debugging of the system to ensure the automated control and smooth operation of the production line. It is also necessary to conduct performance testing and operation tests of the equipment to ensure that the production line has the expected stability and production capacity.